Investing in the Metaverse: Is it the Future of Finance?
The metaverse. This is the phrase that has rippled across the tech world for quite a while, capturing people’s attention. The term conjures images of connected digital worlds, immersive virtual realities, and seemingly endless possibilities. According to a study published in ScienceDirect, “the metaverse has the potential to extend the physical world using augmented and virtual reality technologies allowing users to seamlessly interact within real and simulated environments using avatars and holograms.”
Although the metaverse is still in its infancy, it offers both exciting possibilities and immense challenges to financial institutions and investors.
But what exactly is metaverse, and is it the future of finance? In this blog, we will try to answer these two critical questions in detail.
An Overview of the Metaverse and How It Relates to Finance
In its broadest sense, the metaverse is a network of persistent, shared, 3D virtual worlds that are connected. In these spaces, users can engage with one another, take part in activities, and even own digital assets. And this digital ownership is made possible by blockchain technology and NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), which enable the production and trade of virtual commodities, services, and even real estate. This is where the relationship between finance and the metaverse becomes most intriguing.
In his book The Metaverse and How it Will Revolutionize Everything, Matthew Ball, the CEO of Epyllion, which provides investment and strategic advisory services, produces television, films, and video games, wrote: “the metaverse is a massively scaled and interoperable network of real-time rendered 3D virtual worlds that can be experienced synchronously and persistently by an effectively unlimited number of users with an individual sense of presence, and with continuity of data, such as identity, history, entitlements, objects, communications, and payments.”
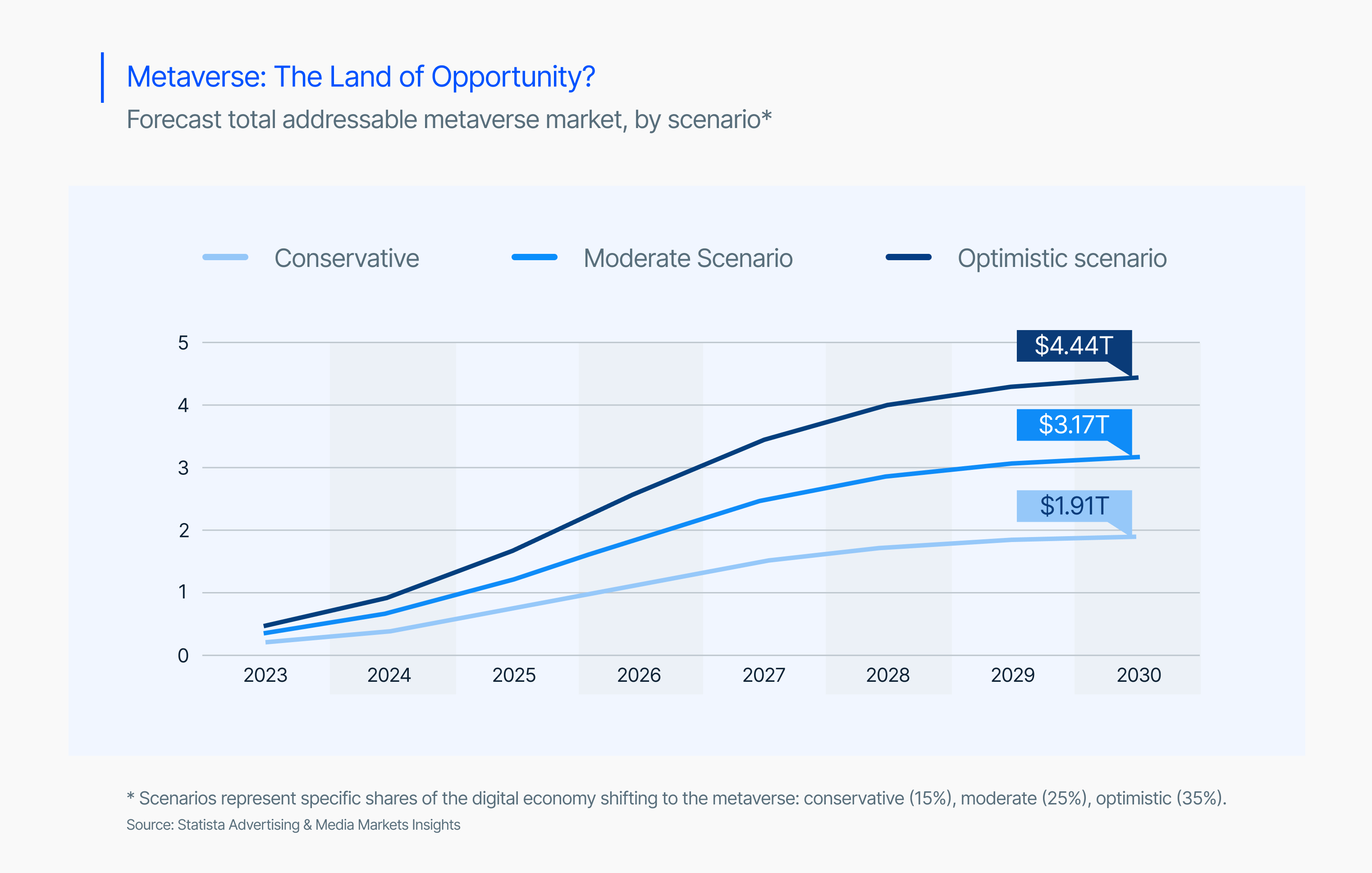
How Big Can the Metaverse Be?
According to Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, Citi and KPMG, the metaverse’s economy is likely to range between $8-13 trillion dollars over time. As per the World Economic Forum and IMF estimates, the digital economy in 2021 was roughly 15% of world GDP. Over the next decade, growth of the metaverse can help push that 15% higher, possibly to 20-25%, which will help create substantial economic value.
Opportunities for Financial Innovation in the Metaverse
The potential for new markets and economic models is one of the metaverse's most compelling features. Consider trading digital art, purchasing and selling virtual land, or even conducting business in a virtual setting. This is not merely a fantasy of the future; it is now taking place. Users can buy and build virtual land on platforms like Decentraland and The Sandbox, giving businesses the chance to have a presence and engage with clients in completely new ways. The distinction between the real and virtual worlds is further blurred by the fact that these virtual economies are frequently driven by their own cryptocurrencies.
In addition, the metaverse offers the potential for decentralized finance (DeFi) to thrive. Built on blockchain technology, DeFi platforms aim to provide financial services without intermediaries like banks. In the metaverse, these platforms could enable users to lend, borrow, and invest cryptocurrencies and other digital assets seamlessly within the virtual world, potentially creating more efficient markets.
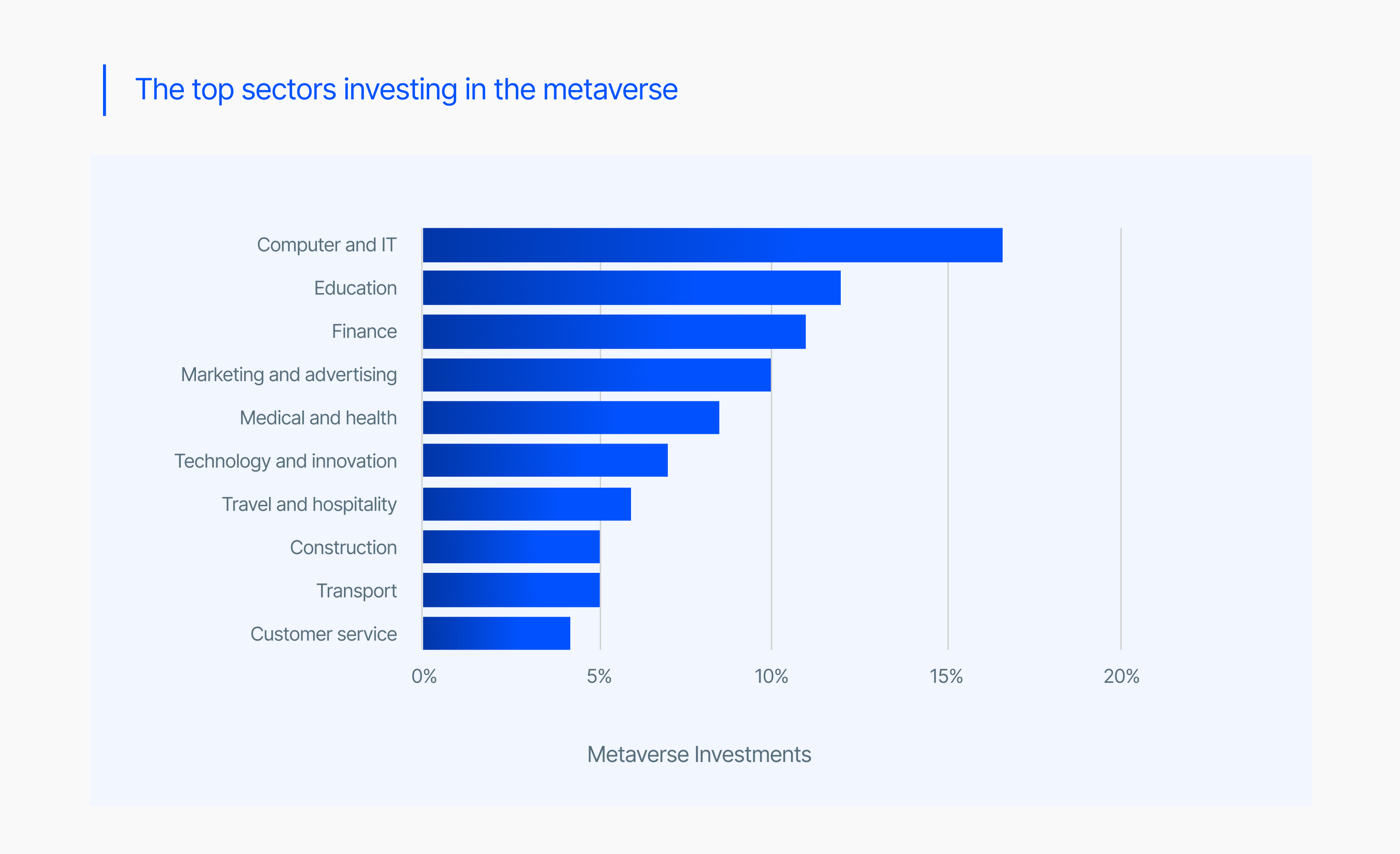
Challenges and Risks Associated with Metaverse Investments
Despite all the upsides mentioned above, the metaverse has its fair share of challenges, including the lack of interoperability between different metaverse platforms. Currently, assets and experiences are often limited to specific virtual worlds, restricting their value and impeding the development of a truly unified metaverse.
Another important concern is the volatile and abstract nature of many metaverse-related assets. The value of cryptocurrencies and NFTs can drastically vary, making them risky investments. This volatility is worsened by the relatively illiquid nature of some of these markets, making it difficult to buy and sell large quantities of assets without substantially affecting prices.
The other major issue is security. Because it’s closely integrated with finance, it becomes a more attractive target for hackers and swindlers. Therefore, it’s all essential to protect user data and ensure the security of digital assets of metaverse-based financial services.
The Takeaway
Although investing in the metaverse presents opportunities for development and creativity, it also involves significant risks. Key risks associated with metaverse investments include technological anomalies, regulatory obstacles, user adoption challenges, security concerns, market volatility, lack of standardization, intellectual property infringement, monetization difficulties, reliance on external platforms, and unproven business models.
If you’re looking to participate in the metaverse's growth and seeking viable investment options, potential avenues include companies operating in gaming and entertainment sectors, blockchain and cryptocurrency projects, and virtual assets. If you are a graphic designer, you can buy or sell your metaverse avatar at platforms like TokenMinds. For non-fungible tokens (NFTs), you can purchase available tokens at Binance or any other platform dealing in similar assets. Also, if you are an investor and are accustomed to taking long-term paradigm bets, Earth 2 appears to be the new real estate windfall.
Share With